13. Randomized Algorithms¶
约 1649 个字 17 行代码 预计阅读时间 8 分钟
efficient randomized algorithms that only need to yield the correct answer with high probability
randomized algorithms that are always correct, and run efficiently in expectation
13.1 The Hiring Problem¶
-
Hire an office assistant from headhunter
-
Interview a different applicant per day for N days
-
Interviewing\(Cost = C_i << Hiring Cost = C_h\)
\(面试成本 = C_i << 招聘成本 = C_h\)
- Analyze interview & hiring cost instead of running time
分析面试和招聘成本而不是运行时间
Assume M people are hired. Total Cost:\(O(NC_i + MC_h)\)
int Hiring ( EventType C[ ], int N )
{ /* candidate 0 is a least-qualified dummy candidate */
int Best = 0;
int BestQ = the quality of candidate 0;
for ( i=1; i<=N; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i ); /* Ci */
if ( Qi > BestQ ) {
BestQ = Qi;
Best = i;
hire( i ); /* Ch */
}
}
return Best;
}
worse case: The candidates come in increasing quality order.
最坏的情况是:面试者的素质一次递增,相当于每面试一个人,就会招募一个人
时间复杂度为:\(O(NC_h)\)
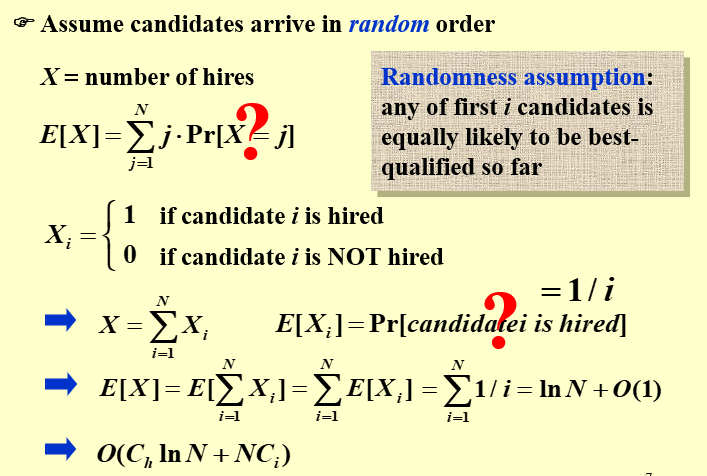
Assume candidates arrive in random order
Randomness assumption: any of first i candidates is equally likely to be best-qualified so far.
随机性假设:到目前为止,前 i 名候选人中的任何一个都同样可能最有资格
前i个候选人,任何一个都可能被录取。以第i个人为例,第i个人被录取,意味着它的能力比前面所有人的能力都强,此时的概率是1/i,对应的期望就是1*1/i + 0*(i-1)/i = 1/i
所以最终的期望为\(E[X] = E[\sum_{i=1}^NX_i] = \sum_{i=1}^NE[X_i] = \sum_{i=1}^N \dfrac{1}{i} = lnN\)。付出的总代价为\(O(C_hlnN+NC_i)\)
int RandomizedHiring ( EventType C[ ], int N )
{ /* candidate 0 is a least-qualified dummy candidate */
int Best = 0;
int BestQ = the quality of candidate 0;
randomly permute the list of candidates;
for ( i=1; i<=N; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i ); /* Ci */
if ( Qi > BestQ ) {
BestQ = Qi;
Best = i;
hire( i ); /* Ch */
}
}
}
13.1.1 Randomized Permutation Algorithm¶
13.1.2 Online Hiring Algorithm¶
hire only once
int OnlineHiring ( EventType C[ ], int N, int k)
{
int Best = N;
int BestQ = - ;
for ( i=1; i<=k; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i );
if ( Qi > BestQ ) BestQ = Qi;
}
for ( i=k+1; i<=N; i++ ) {
Qi = interview( i );
if ( Qi > BestQ ) {
Best = i;
break;
}
}
return Best;
}
前面k个人仅用于测试评估面试者的水平(挑选出最高的素质),雇佣人从k+1个人开始,每个人的quality都与最高的的quality进行比较,选择出最好的
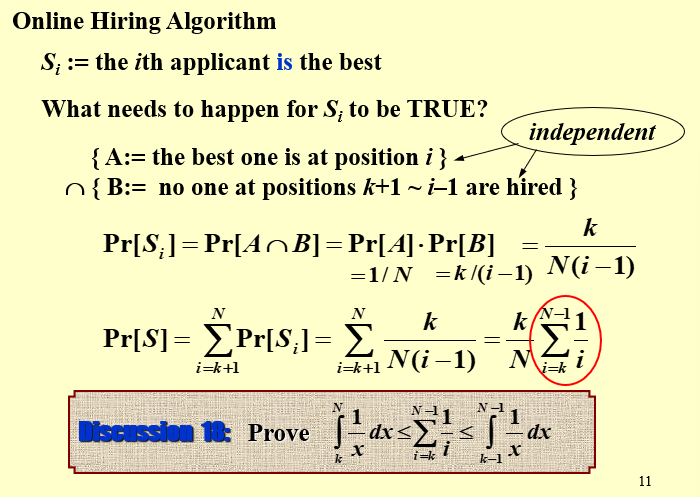
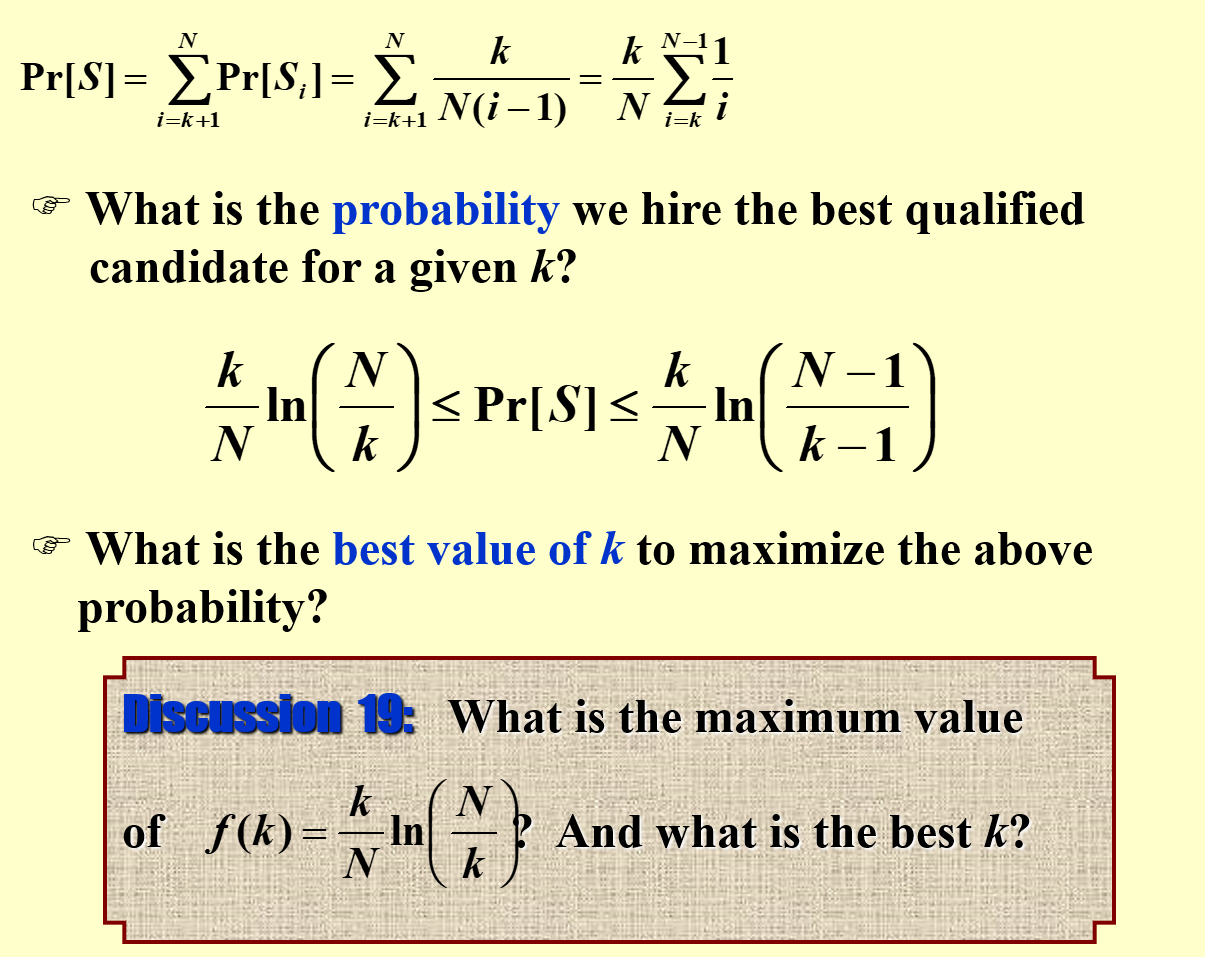
What is the probability we hire the best qualified candidate for a given k?
最好的面试者在第i个位置,要求i>k,并且从k+1到i-1的面试者都没有被雇佣
What is the best value of k to maximize above probability?
-
用\(S_i\)表示第\(i\)个候选者是最好的
-
要使第\(i\)个人是最好的,需要满足第\(i\)个人首先quality需要大于bestQ,然后从\(k+1\)到\(i-1\)个人没有人的quality大于bestQ,也就是说没有人被hire(
因为从上方代码可以看出一旦某个人的quality大于bestQ,就会break)
从第\(k+1\)到第\(i-1\)没有录于任何人。这意味着前\(i-1\)个人里面,最好的落在了前\(k\)个人之中,概率就是\(\dfrac{k}{i-1}\)
-
此时概率为\(P[S_i] = P[A\cap B] = P[A]\times P[B] = \dfrac{1}{N} \times \dfrac{k}{i-1} = \dfrac{k}{N(i-1)}\)
-
那么最好的面试者出现在第\(k\)个人之后的概率为: $$ P[S] = \sum_{i=k+1}^N P[S_i] = \sum_{i=k+1}^N \dfrac{k}{N(i-1)} = \dfrac{k}{N}\sum_{i=k}^{N-1} \dfrac{1}{i} $$
13.2 Quicksort¶
-
Deterministic Quicksort
-\(\Theta(N^2)\)
worst-case running time-\(\Theta(N logN)\)average case running time
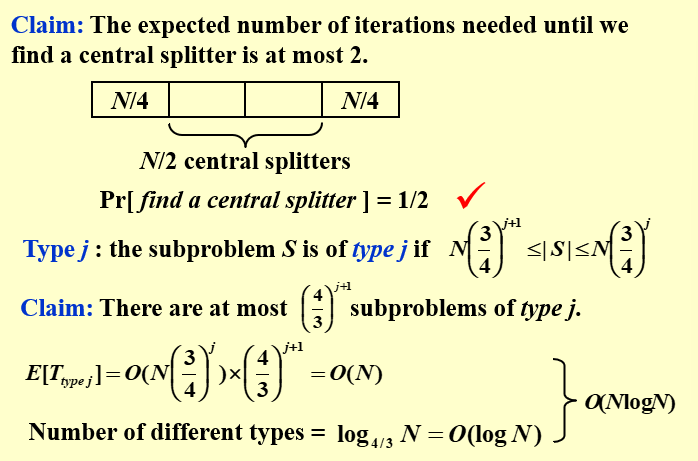
要想加速quicksort,每一次将数据一分为二时,希望两边的数据大致相等
Central splitter := the pivot that divides the set so that each side contains at least n/4
Central splitter := 划分集合的主元,使得每边至少包含 n/4
Modified Quicksort := always select a central splitter before recursions
相当于选择pivot的范围在[n/4,3n/4].选择到central splitter的概率是1/2
如果第一次没有选择到,就再次选择。期望次数为:
划分j次之后,子问题的最大尺寸是\(N (\dfrac{3}{4})^{j+1} \leq |S| \leq N (\dfrac{3}{4})^{j}\)
按照子问题的最大尺寸来,相应的子问题的最大数量为\((\dfrac{4}{3})^{j+1}\),此时恰好,子问题的数量乘以子问题的规模得到N
解决类型j所需的时间复杂度为:\(E[T_{type \ j}] = O(N(\dfrac{3}{4})^j)\times (\dfrac{4}{3})^{j+1} = O(N)\)
其中问题的类型是\(log_{\frac{4}{3} }N\),因为问题的最小规模需要为1
所以总的期望时间复杂度为\(O(N) \times O(logN) = O(NlogN)\)
13.3 习题集¶
-
Let\(a=\left(a_{1}, a_{2}, \ldots, a_{i}, \ldots, a_{j}, \ldots, a_{n}\right)\)denote the list of elements we want to sort. In the quicksort algorithm, if the pivot is selected uniformly at random. Then any two elements get compared at most once and the probability of\(a_{i}\)and\(a_{j}\)being compared is\(2 /(j-i+1)\)for\(j>i\), given that\(a_{i}\)or\(a_{j}\)is selected as the pivot. (T/F)
F举反例如下:{3, 4, 1, 2, }。如果第一次选pivot选中3或者2,那么1和4会被分开,不会被比较。
如果第一次就选中1或4,它们才会被比较。因此它们被比较的概率是1/2。按照\(\dfrac{2}{j-i+1}\)计算,应该是1。
事实上,如果是已经被排序好的,这就是对的。
-
Given a linked list containing\(N\)nodes. Our task is to remove all the nodes. At each step, we randomly choose one node in the current list, then delete the selected node together with all the nodes after it. Here we assume that each time we choose one node uniformly among all the remaining nodes. What is the expected number of steps to remove all the nodes?
A.\(\Theta (\log N)\)
B.\(N/e\)
C.\(N/2\)
D.\(\sqrt{N}\)
A- 初始时,链表有 𝑁N 个节点。
- 在每一步中,我们随机选择当前链表中的一个节点,删除该节点及其之后的所有节点。
- 目标是计算完全删除链表中所有节点所需的预期步骤数。
假设 𝐸(𝑁)表示从有 𝑁 个节点的链表中删除所有节点所需的预期步骤数
如果我们选择第 𝑖 个节点(其中 𝑖 的范围是从 1 到 𝑁 ),则该选择会删除从第 𝑖 个节点到末尾的所有节点。因此,在这一步中删除了\(𝑁−𝑖+1\)个节点。
首先先在N个点中任选一个点,执行一步操作,假设选取第i个点,那么剩余的点为i-1,后续只需要求E(i-1)那么得到递归关系式:\(E(N) = 1 + \dfrac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^NE(i-1) = 1 + \dfrac{1}{N}\sum_{i=0}^{N-1}E(i)\)
-
直接代入 B,C,显然不对。事实上,可以看到这种递推式只可能出有理数,D 很可能出无理数,也不对。
-
然而,很轻松就可以通过强归纳法判断\(a_n=O(\log N)\)。(\(\Omega\)没有试过,应该也可以。) $$ a_n = \frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^{N-1}a_i+1 \leqslant \frac{C}{N}\log\left(2N\prod_{i=1}^{N-1}i\right) \leqslant C\log N $$ 这里的第二个不等号并不那么严格,不过\(N\)足够大的时候一定是严格的。
-
Use The Online Hiring Algorithm ( hire only once ). Assume that the quality input\(C[ ]\)is uniformly random.
int OnlineHiring ( EventType C[ ], int N, int k ) { int Best = N; int BestQ = -INFINITY ; for ( i=1; i<=k; i++ ) { Qi = interview( i ); if ( Qi > BestQ ) BestQ = Qi; } for ( i=k+1; i<=N; i++ ) { Qi = interview( i ); if ( Qi > BestQ ) { Best = i; break; } } return Best; }When\(N = 271\)and\(k = 90\), the probability of hiring the Nth candidate is __.
1/3。要求前 270 人中最好的落在前 90 人中。也可以分前 271 人中最好的在哪里进行讨论,即
\[ \frac{1}{N}\cdot \frac{k}{N-1} + \frac{k}{N} = \frac{1}{3} \]