5. Binomial Queue¶
约 2631 个字 337 行代码 预计阅读时间 17 分钟
为什么需要二项堆?
二项堆的引入来源于我们希望插入建堆的操作有常数的平均时间。因为
二项堆能够实现在$O(N)$的时间内实现$n$个结点的插入操作。
5.1 概念¶
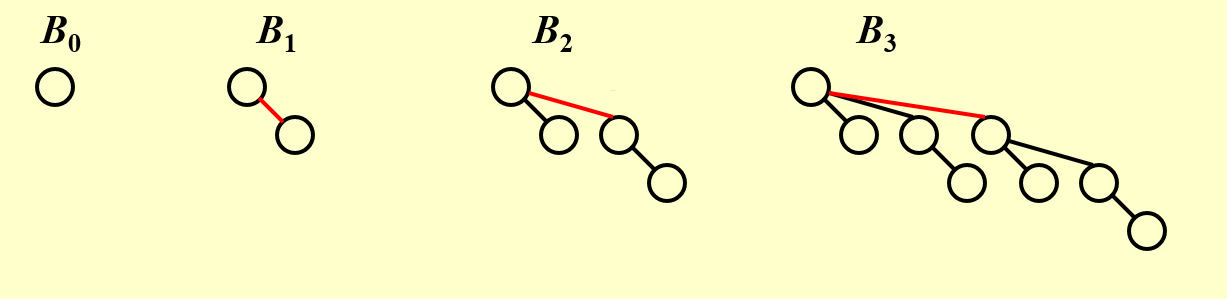
A binomial queue is not a heap-ordered tree, but rather a collection of heap-ordered trees, known as aforest. Each heap-ordered tree is a binomial tree.
二项式队列不是堆有序树,而是堆有序树的集合,称为森林。每个堆排序树都是一个二项式树。
A binomial tree of height 0 is a one-node tree.
A binomial tree, \(B_k\), of height k is formed by attaching a binomial tree, \(B_{k – 1}\), to the root of another binomial tree,\(B_{k – 1}\).
二项堆的定义如下:
-
结构性质
- 二项堆不再是一棵树,而是多棵树构成的森林,其中每一棵树都是二项树
- 一个二项堆中的每一棵二项树都具有不同的高度,即每一高度最多对应一颗二项树
- 高度为0的二项树是一个单节点树。高度为k的二项树\(B_k\)通过将一棵二项树\(B_{k-1}\)连接到另一棵二项树\(B_{k-1}\)的根上形成。
-
序性质:
每一棵二项树都保持堆的序性质(有序堆),对于最小堆——孩子结点大于父亲结点
从图中我们可以观察出二项树\(B_k\)实际上是由一个root加上\(B_0,B_1,...B_{k-1}\)组成
用数学归纳法证明 \(B_k\) 有 \(2^k\)个结点
-
当k=0时,显然一个结点成立
-
当k=m时,假设条件成立。那么当k=m+1时,
\(B_{m+1}\)的结点数是\(2^0+2^1+...+2^m + 1 = 2 ^{m+1} - 1 + 1 = 2 ^{m+1}\)
用数学归纳法证明在深度为\(d\)的结点数恰好是二项系数\(C_n ^d\)
根据二项树的定义:B_k是由两个B_{k-1}形成的,且两棵树存在深度差1
\(B_k\) structure + heap order + one binomial tree for each height
A priority queue of any size can be uniquely represented by a collection of binomial trees.
5.2 操作¶
5.2.1 FindMin¶
The minimum key is in one of the roots.
There are at most \(logN\) roots, hence \(Tp\) =\(O(logN)\).
最小值在二项队列的某一个根结点,只需遍历所有的root
We can remember the minimum and update whenever it is changed. Then this operation will take O(1).
设置专门记录最小根结点的结点,只需要在DeleteMin或则Insert 一个新的最小值后更新这个临时结点即可。时间复杂度为\(O(1)\)
5.2.2 Merge¶
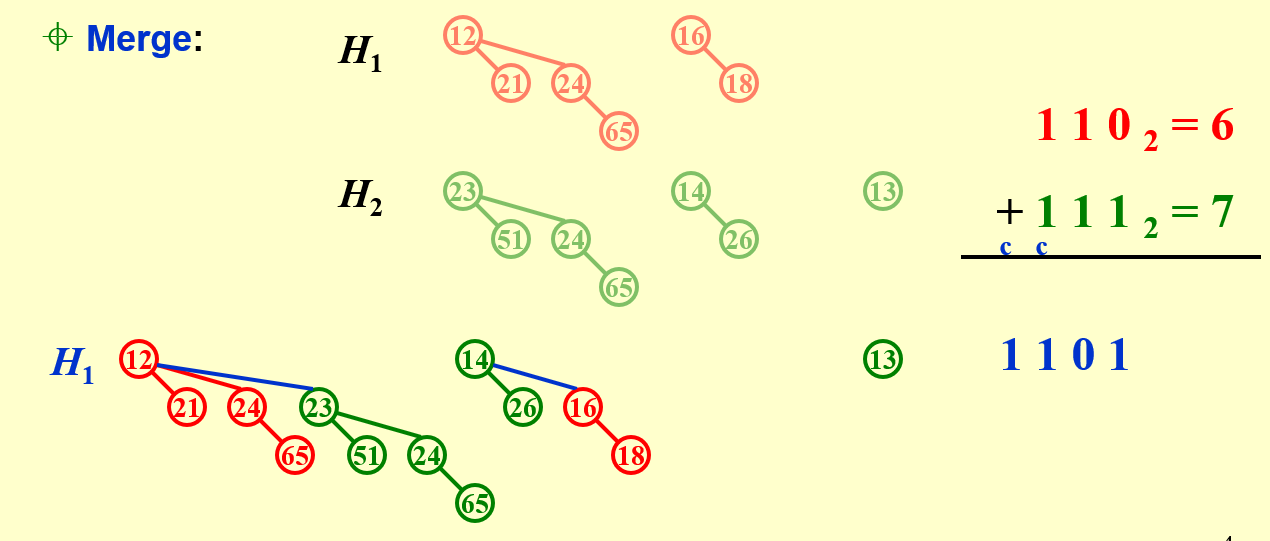
每一个二项堆都有一个唯一对应的二进制数。那么合并二项堆实际上可以等价于二进制数的加法。
从最小的二项树开始(也就是二进制的最低位),如果无需进位(0+1,1+0)则直接留下作为新堆的一部分。如果需要进位(1+1),在合并后与下一位做加法,如此循环到最高位完成操作。
在保证堆的存储顺序是按高度从小到大排列的前提(这样就不用先遍历所有的堆,找到最小的堆。而是直接从开头进行合并)下,时间复杂度很显然就是\(O(log n)\),因为就是二进制逐位做操作,只需要计算一共有多少二进制位即可,O(logN)
Must keep the trees in the binomial queue sorted by height.
相应\(B_k\) merge的时候,需要满足heap上小下大的要求。root大的作为root小的子树
// 二项树的合并
BinTree MergeTrees(BinTree T1, BinTree T2)
{
// merge equal size trees
// attach the larger one to the smaller one
if(T1->Element > T2->Element)
return MergeTrees(T2, T1);
// T2 is larger, attach T2 to T1
T2->NextSibling = T1->LeftChild;
T1->LeftChild = T2;
return T1;
}
// 二项队列的合并
BinQueue Merge(BinQueue H1, BinQueue H2)
{
BinTree T1, T2, Carry = NULL;
if(H1->currentsize + H2->currentsize > 100)
cout << "Merge would exceed max tree capacity!" << endl;
H1->currentsize += H2->currentsize;
for(int i = 0, j = 1; j <= H1->currentsize; i++, j *= 2)
{
T1 = H1->TheTrees[i];
T2 = H2->TheTrees[i];
switch(4 * !!Carry + 2 * !!T2 + !!T1)
{
// Carry T2 T1
case 0: // 000 no tree
break;
case 1: // 001 only T1
break;
case 2: // 010 only T2
H1->TheTrees[i] = T2;
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 3: // 011 T1 and T2
Carry = MergeTrees(T1, T2);
H1->TheTrees[i] = H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 4: // 100 only Carry
H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry;
Carry = NULL;
break;
case 5: // 101 Carry and T1;
Carry = MergeTrees(Carry, T1);
H1->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 6: // 110 Carry and T2
Carry = MergeTrees(Carry, T2);
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 7: // 111 all three
H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry;
Carry = MergeTrees(T1, T2);
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
}
}
return H1;
}
-
这里使用
!!的目的是将指针bool化,如果T1存在,!!T1就等于1,如果T2不存在,那么!!T2就等于0 -
然后我们就能理解\(4\times !!Carry + 2\times !!T2+!!T1\) 的含义了,事实上这就是一个三位二进制数(当然case 的 标号还是十进制的,但我们心里要转化为二进制来分析),最高位表示是否有carry,即
之前的合并是否带来了进位(从堆的角度看也就是之前合并出了一棵新的更高的二项树),第二位代表第二个堆H2是否有高度为i 的二项树,最后一位代表H1 是否有高度为i 的二项树。 -
不同case对应的情况
- 000:什么都不用做
- 001:\(T1\)存在,既然返回的就是\(H1\),所以什么都不用做
- 010:\(T2\)存在,但是由于返回的是\(H1\),需要将\(H2\)中的树转移到\(H1\)中对应的树,同时\(H2\)对应的树需要置为NULL
- 011:\(T1\),\(T2\)都存在,此时会产生carry,\(H1\) 和 \(H2\) 当前位变为NULL,进位等于两个堆该高度的二项树合并后的结果
- 100:仅仅carry存在,类比010
- 101:\(H1\) 当前位变为NULL,新的carry 等于\(T1\) 和当前的carry 合并的结果
- 110:\(H2\) 当前位变为NULL,新的carry 等于\(T2\) 和当前的carry 合并的结果
- 111:此让\(H1\) 当前位变为carry,新的carry 等于\(T1\) 和\(T2 \(合并的结果,最后给\)H2\) 当前位变为NULL 即可。
5.2.3 Insert¶
看作是merge的special case
【Example】Insert 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 into an initially empty queue.
- 1,2 形成一个\(B_1\)
- 3,4形成一个\(B_1\),与前面的1,2 merge 形成\(B_2\)
- 5,6形成一个\(B_1\)
- 7形成一个\(B_0\)
BinQueue Insert(BinQueue H1, int x)
{
BinQueue OneItem;
BinTree T;
OneItem = Initialize();
T = new BinNode;
if(T == NULL)
cout << "Out of space!" << endl;
T->Element = x;
T->LeftChild = T->NextSibling = NULL;
OneItem->TheTrees[0] = T;
OneItem->currentsize = 1;
return Merge(H1, OneItem);
}
5.2.4 DeleteMin¶
时间复杂度为\(O(log N)\)
在根结点找到最小值,然后把最小值所在的树单独拿出分裂为二项队列,然后把这个新的二项队列与原二项队列进行合并。每一个过程的时间复杂度为\(O(logN)\)。故加起来的时间复杂度仍为\(O(logN)\)。
int DeleteMin(BinQueue H)
{
BinQueue DeletedQueue;
Position DeletedTree, OldRoot;
int MinItem = 1000000;
int i, j, MinTree;
// MinTree is the index of thr tree with the minimum item
if(Isempty(H))
{
cout << "Empty binomial queue!" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 1. find the tree with the minimum item
for(i = 0; i < MaxTrees; i++)
{
if(H->TheTrees[i] && H->TheTrees[i]->Element < MinItem)
{
MinItem = H->TheTrees[i]->Element;
MinTree = i;
}
}
DeletedTree = H->TheTrees[MinTree];
// 2. remove the MinTree from H
H->TheTrees[MinTree] = NULL;
// 3. remove the MinItem from the MinTree
// and store the rest of the MinTree in DeletedQueue
OldRoot = DeletedTree;
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->LeftChild;
delete OldRoot;
DeletedQueue = Initialize();
// 对于索引为i的树,其包含的节点数为2^i
DeletedQueue->currentsize = (2 ^ MinTree) - 1;
for(j = MinTree - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j] = DeletedTree;
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->NextSibling;
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j]->NextSibling = NULL;
}
H->currentsize -= DeletedQueue->currentsize + 1;
H = Merge(H, DeletedQueue);
return MinItem;
}
5.3 二项队列的实现¶
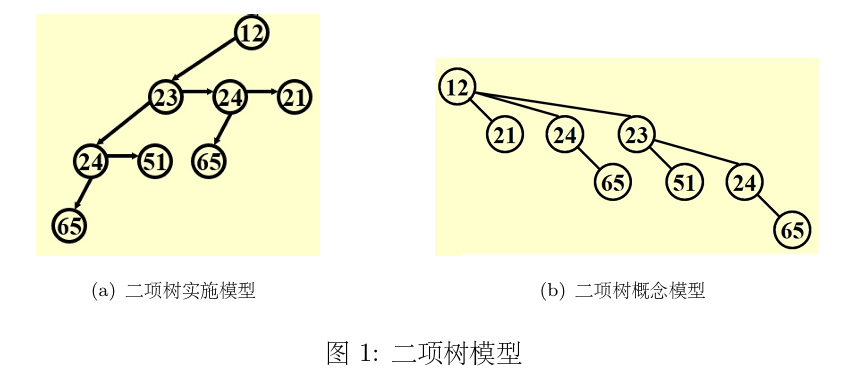
为什么使用左儿子右兄弟模型?
因为每一个结点的孩子数量可能大于2个
要从根结点12开始快速遍历三个子树(21,24,23),要用“左孩子右兄弟的实现方式,对应12->23->24->21
图(b)\(B_3\)是两棵\(B_2\)的合并结果,为什么合并之后需要按照子树的大小(结点数)降序排列呢?
根结点为12和23的两棵树合并时,23会成为12的子树。按照左儿子右兄弟的模型,应该将23插入到子树的链表。
如果按照升序的话,需要先遍历所有的子结点(21,24),才能将最大子树\(B_2\)加上,多出来遍历的开支。
#include "BinTree.h"
using namespace std;
// #define MaxTrees 10
// typedef struct BinNode
// {
// int Element;
// // 左儿子右兄弟
// Position LeftChild;
// Position NextSibling;
// }*BinTree, *Position;
// typedef struct Collection
// {
// // total number of nodes
// int currentsize;
// BinTree TheTrees[MaxTrees];
// }*BinQueue;
// int IsEmpty(BinQueue H);
// BinQueue Initialize();
// BinTree MergeTrees(BinTree T1, BinTree T2);
// BinQueue Insert(BinQueue H1, int x);
// BinQueue DeleteMin(BinQueue H);
// void PrintQueue(BinQueue H);
int Isempty(BinQueue H)
{
return H->currentsize == 0 || H == NULL;
}
BinQueue Initialize()
{
BinQueue H = new Collection;
if(H == NULL)
cout << "Out of space!" << endl;
H->currentsize = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < MaxTrees; i++)
H->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
return H;
}
BinTree MergeTrees(BinTree T1, BinTree T2)
{
// merge equal size trees
// attach the larger one to the smaller one
if(T1->Element > T2->Element)
return MergeTrees(T2, T1);
// T2 is larger, attach T2 to T1
T2->NextSibling = T1->LeftChild;
T1->LeftChild = T2;
return T1;
}
BinQueue Merge(BinQueue H1, BinQueue H2)
{
BinTree T1, T2, Carry = NULL;
if(H1->currentsize + H2->currentsize > 100)
cout << "Merge would exceed max tree capacity!" << endl;
H1->currentsize += H2->currentsize;
for(int i = 0, j = 1; j <= H1->currentsize; i++, j *= 2)
{
T1 = H1->TheTrees[i];
T2 = H2->TheTrees[i];
switch(4 * !!Carry + 2 * !!T2 + !!T1)
{
// Carry T2 T1
case 0: // 000 no tree
break;
case 1: // 001 only T1
break;
case 2: // 010 only T2
H1->TheTrees[i] = T2;
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 3: // 011 T1 and T2
Carry = MergeTrees(T1, T2);
H1->TheTrees[i] = H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 4: // 100 only Carry
H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry;
Carry = NULL;
break;
case 5: // 101 Carry and T1;
Carry = MergeTrees(Carry, T1);
H1->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 6: // 110 Carry and T2
Carry = MergeTrees(Carry, T2);
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 7: // 111 all three
H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry;
Carry = MergeTrees(T1, T2);
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
}
}
return H1;
}
BinQueue Insert(BinQueue H1, int x)
{
BinQueue OneItem;
BinTree T;
OneItem = Initialize();
T = new BinNode;
if(T == NULL)
cout << "Out of space!" << endl;
T->Element = x;
T->LeftChild = T->NextSibling = NULL;
OneItem->TheTrees[0] = T;
OneItem->currentsize = 1;
return Merge(H1, OneItem);
}
int DeleteMin(BinQueue H)
{
BinQueue DeletedQueue;
Position DeletedTree, OldRoot;
int MinItem = 1000000;
int i, j, MinTree;
// MinTree is the index of thr tree with the minimum item
if(Isempty(H))
{
cout << "Empty binomial queue!" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 1. find the tree with the minimum item
for(i = 0; i < MaxTrees; i++)
{
if(H->TheTrees[i] && H->TheTrees[i]->Element < MinItem)
{
MinItem = H->TheTrees[i]->Element;
MinTree = i;
}
}
DeletedTree = H->TheTrees[MinTree];
// 2. remove the MinTree from H
H->TheTrees[MinTree] = NULL;
// 3. remove the MinItem from the MinTree
// and store the rest of the MinTree in DeletedQueue
OldRoot = DeletedTree;
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->LeftChild;
delete OldRoot;
DeletedQueue = Initialize();
// 对于索引为i的树,其包含的节点数为2^i
DeletedQueue->currentsize = (2 ^ MinTree) - 1;
for(j = MinTree - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j] = DeletedTree;
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->NextSibling;
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j]->NextSibling = NULL;
}
H->currentsize -= DeletedQueue->currentsize + 1;
H = Merge(H, DeletedQueue);
return MinItem;
}
void PrintTree(BinTree T)
{
// 关于左儿子右兄弟的遍历
// 一行一行的输出
queue<BinTree> line1;
queue<BinTree> line2;
line1.push(T);
while(!line1.empty())
{
BinTree temp = line1.front();
line1.pop();
cout << temp->Element << " ";
if(temp->LeftChild)
line2.push(temp->LeftChild);
while(temp->NextSibling)
{
cout << temp->NextSibling->Element << " ";
if(temp->NextSibling->LeftChild)
line2.push(temp->NextSibling->LeftChild);
temp = temp->NextSibling;
}
if(line1.empty())
{
cout << endl;
swap(line1, line2);
}
}
}
void PrintQueue(BinQueue H)
{
for(int i = 0; i < MaxTrees; i++)
{
if(H->TheTrees[i])
{
cout << "Tree " << i << ": "<< endl;
PrintTree(H->TheTrees[i]);
}
}
cout << "--------------------------\n";
}
int main()
{
BinQueue H1 = Initialize();
H1 = Insert(H1, 12);
H1 = Insert(H1, 21);
H1 = Insert(H1, 24);
H1 = Insert(H1, 65);
H1 = Insert(H1, 23);
H1 = Insert(H1, 51);
H1 = Insert(H1, 24);
H1 = Insert(H1, 65);
H1 = Insert(H1, 14);
H1 = Insert(H1, 26);
H1 = Insert(H1, 16);
H1 = Insert(H1, 18);
H1 = Insert(H1, 13);
PrintQueue(H1);
int MinItem = DeleteMin(H1);
PrintQueue(H1);
cout << "MinItem: " << MinItem << endl;
}
5.4 摊还分析¶
A binomial queue of N elements can be built by N successive insertions in O(N) time.
插入最坏的情况是\(O(log N)\),但是坏操作带来进位的同时,后续会带来很多的0,也就没有进位
5.4.1 聚合法¶
聚合法需要每一步的操作复杂度。关于合并的时间复杂度实际上与二进制的加法有对应关系。包含加法和进位,对应就是插入和merge。这两种情况都对应常数时间复杂度。
从空树连续插入n个顶点的时间复杂度为 n + 进位的次数。
最低位每次加1都会merge(对应单纯的插入),次低位每两次插入会merge(对应进位),以此类推,计算n次插入造成的merge次数 $$ n + \dfrac{n}{2} + \dfrac{n}{4}+...+\dfrac{n}{2^{logn +1}} $$ 根据等比数列的求和,显然上述的时间复杂度不会超过2n,所以单步操作的摊还时间成本就是常数级的。
此处的total link可以理解为:
每两次发生一次\(B_0->B_1\)的link,每四次发生一次\(B_1->B_2\)的link,依次类推\(N(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{8}+....)\)
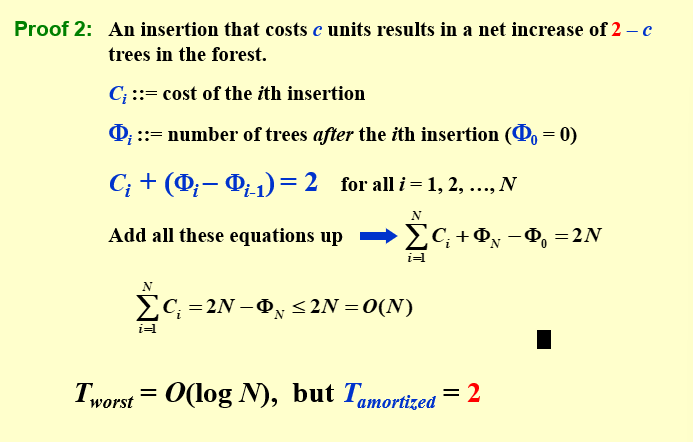
5.4.2 势能法¶
分析得到
-
link=1,不会造成二项树的增加(\(B_0 \rightarrow B_1\))。
-
link=2,会造成二项树数量减1(\(B_0\rightarrow B_1 \rightarrow B_2\)),原先的\(B_0,B_1\)被转化为\(B_2\)
- 依次类推,link=3,会造成二项树的数量减2
每一步的时间复杂度为step+link,得到如果一次插入的时间复杂度为k,那么二项队列中的二项树将减少$(k-2)$
记\(c_i\)表示实际上每一步插入的成本
记\(\Phi_i\)表示在第i次插入完成后,二项队列中二项树的数量
那么每次的摊还成本就是 $$ \widehat c_i = c_i + \Phi_i - \Phi_{i-1} = c_i + (2-c_i) = 2 $$
5.5 习题集¶
-
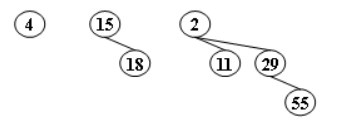
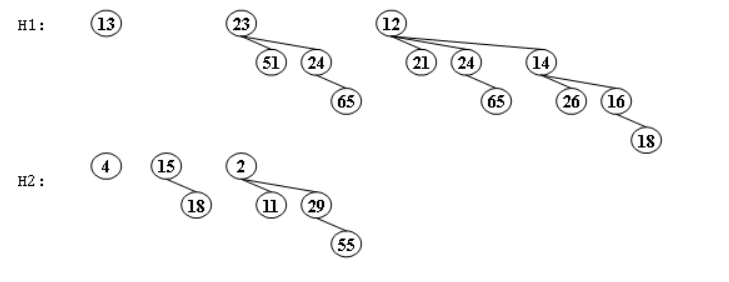
Delete the minimum number from the given binomial queues in the following figure. Which one of the following statements must be FALSE?
-
A. there are two binomial trees after deletion, which are \(B_1\) and \(B_2\)
-
B. 11 and 15 can be the children of 4
-
C. 29 can never be the root of any resulting binomial tree -
D. if 29 is a child of 4, then 15 must be the root of \(B_1\)
此处说明进位carry和H1,H2的计算方式是不固定的,可以自由组合,得到不同的结果
-
-
Merge the two binomial queues in the following figure. Which one of the following statements must be FALSE?
-
A. there are two binomial trees after merging, which are \(B_2\) and \(B_4\)
-
B. 13 and 15 are the children of 4
-
C. if 23 is a child of 2, then 12 must be another child of 2
-
D. if 4 is a child of 2, then 23 must be another child of 2
-
-
Inserting a number into a binomial heap with 15 nodes costs less time than inserting a number into a binomial heap with 19 nodes.
False\(15 = 1111_2, 19 = 10011_2\)
显然插入到19个node的二项堆发生的进位次数少
-
To implement a binomial queue, the subtrees of a binomial tree are linked in increasing sizes.
False按照子树大小(结点数)降序排列
-
The potential function Q of a binomial queue is the number of the trees. After merging two binomial queues \(H1\) with 12 nodes and \(H2\) with 13 nodes,what is the potential change \(Q(H1+H2)−(Q(H1)+Q(H2))\) ?
\[ 12 = 1100_2\\ 13 = 1101_2\\ 12 + 12 = 11001\\ \Delta Q = 3 - 2 -3 = -2 \] -
Making N insertions into an initally empty binomial queue takes$ Θ(NlogN)$ time in the worst case.
False插入的最坏情况是\(logN,\) 这是因为需要一直进位上去。而N组数据不可能每插入一个就进位,因此是O(N)
-
After deleting number 14 from a binomial queue of 5 numbers { 12, 13, 14, 23, 24 }, which of the followings is impossible?
A.the LeftChild link of the node 12 is NULL;B. the NextSibling link of the node 12 is NULL;
C. the NextSibling link of node 13 may point to node 23;
D. the LeftChild link of node 24 is NULL;
优先队列里面,只有上下的大小限制,左右谁大谁小没有要求。因此,12一定是根,24一定是最下面的那个,A12一定是有孩子的,错。