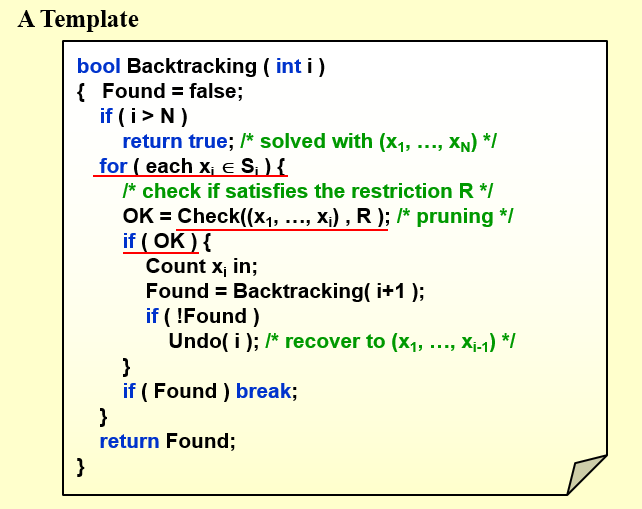
6. Backtracking¶
约 1312 个字 477 行代码 预计阅读时间 13 分钟
6.1 basic idea¶
找到问题答案的一个可靠方法是列出所有候选答案,回溯使我们能够消除对大量候选者的显式检查(剪枝操作),同时仍然保证在算法运行到终止时会找到答案。
basic idea:回溯的历程
生成解,已经生成了前i个解\(((x_1,x_2,...,x_i)),(x_k∈S_k(解空间))\)
要添加新元素\((x_{i+1}^{(1)}∈X_{i+1}(第i个解集))\)
检查是否满足要求,若满足要求则生成解\(((x_1,x_2,...,x_i,x_{i+1}))\)
若不满足则找另一个\((x_{i+1}),若所有的(x_{i+1})\)都不满足条件,那么进行回溯
解变为\(((x_1,x_2,...,x_{i-1}))\)并且标记当前的\((x_i)\)为无效解换下一个\((x_i),\)以此类推
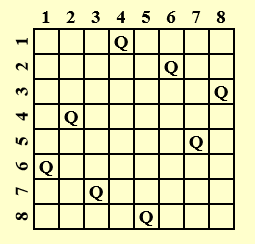
6.2 八皇后问题¶
-
【描述】在棋盘中找到八个位置放置皇后,使得它们都不同行且不同列,也不能同时位于对角线上
\(Q_i\) 表示 queue in the i th row
\(x_i\) 表示 the column index in which \(Q_i\) is $$ solution = (x_1, x_2, x_3, ... x_8) = (4,6,8,2,7,1,3,5) $$
限制条件:
-
\(S_i\) = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 } for 1 <=i <= 8
-
\(x_i != x_j \ if i \ != j\)
不能在同一行和同一列
This implies that the solution must be a permutation of 1, 2, ... , 8. Thus the number of candidates in the solution space is reduced to 8!.
-
\((x_i - x_j) / (i - j) != |1|\)
不能在对角线和反对角线上
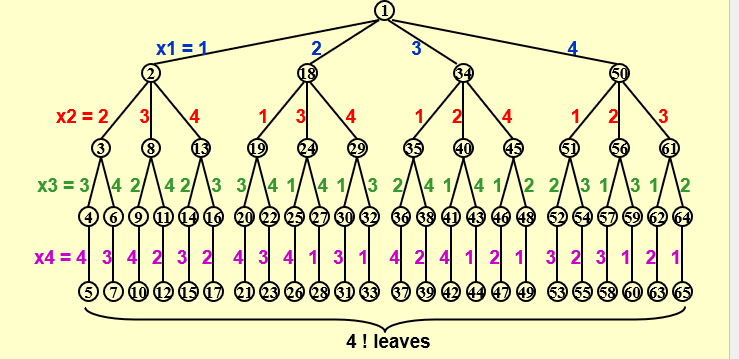
Method: 以4个皇后为例
step 1: 建立一棵game tree
Each path from the root to a leaf defines an element of the solution space.
step 2:执行深度优先搜素,来检查路径是否正确
- 假设x1在第一列,顺序向下,x2 = 2,显然在对角线上,回溯至x1 = 1
- 后续向下,x2 = 3, 显然后续不管x3是在第二列还是第四列都会与x2在对角线上。回溯至x1 = 1
- 向下 x2 =4, 如果后续x3 = 2, x4 =3,在对角线上。如果x3 = 3,x3会与x2在对角线上。
- x1 = 1所有的情况均无法满足条件,继续向上回溯,转化为x1 = 2
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
// 用于控制皇后的数量,棋盘的规模
const int n = 8;
bool Is_safe(vector<int> &board, int row, int col)
{
// check if there is a queen in the same column
// or in the same diagonal
// or in the same anti-diagonal
// row means the row we are going to put a queen
// col means the column we are going to put a queen
// 此时需要用当前的queue的位置和之前的queue的位置进行比较
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
if(board[i] == col || abs(board[i] - col) == abs(i - row))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void SolveNQueens(int row, vector<int> &board, vector<vector<int>> &solutions)
{
// row表示当前要放置皇后的行数
if(row == n)
{
// 说明已经找到了一个解
solutions.push_back(board);
return;
}
// 每一行的皇后的位置都是从0到n-1
// 判断当前的位置是否合法
for(int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
if(Is_safe(board, row, col))
{
board[row] = col;
SolveNQueens(row + 1, board, solutions);
}
}
}
int main()
{
// 初始化棋盘,-1表示没有皇后
// board[i] = j 表示在(i, j)的位置有一个皇后
vector<int> board(n, -1);
// 用于存储所有的解
vector<vector<int>> solutions;
// 执行回溯算法
SolveNQueens(0, board, solutions);
// 输出所有的解
for(auto solution : solutions)
{
for(auto pos: solution)
{
cout << pos << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "Total solutions: " << solutions.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
6.3 高速公路收费问题¶
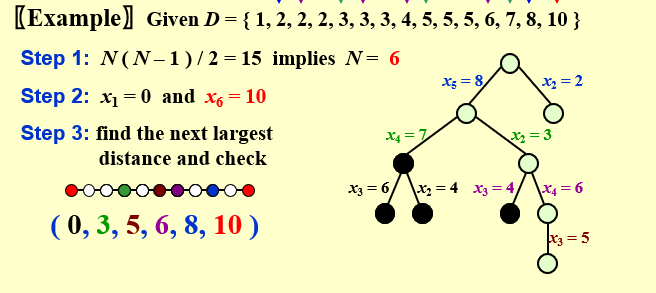
- 【描述】在一条直线上找到n个地方建立加油站,已知它们两两之间的距离,求出所有加油站的位置,假定第一个加油站的坐标是0
Given N points on the x-axis with coordinates \(x1 < x2 < …< xN\) . Assume that \(x1 = 0\). There are \(N( N – 1 ) / 2\) distances between every pair of points.
-
【Solution】
- 通过n(n-1)/2个距离算出n
- 0和最大距离说明都都有加油站
- 从D集合中找最大的进行构建,找了就从D中删除距离,失败的话就回到上一种情况.
- 每次检验分成靠左边和靠右边两个情况
-
首先根据15个距离,算出一共有6个收费站
-
计算首尾两个收费站的坐标 \(x1 = 0, x6 = 10\)
-
find the next largest distance and check
对于长度8,仅可能出现在\(x1\)到\(x5\)或者\(x2\)到\(x6\)
- \(x5 - x1 = 8\) 说明\(x5 = 8\)
- \(x6 - x2 = 8\) 说明\(x2 = 2\)
假设我们现在选取\(x5 =8\), 后续的最大值变为7,仅可能出现在\(x1\)到\(x4\)或者\(x2\)到\(x6\)
- \(x4 - x1 = 7\) 说明 \(x4 = 7\)
- \(x6 - x2 = 7\) 说明$ x2 = 3$
假设我们现在选取\(x4 = 7\),后续的最大值变为6,尽可能出现在\(x1\)到\(x3\)和\(x2\)到\(x6\)
- \(x3 - x1 = 6\) 说明\(x3 = 6\).但是\(x3\)与\(x4\)距离为1,\(x4\)与\(x5\)距离为1,距离表中没有两个1,矛盾
- \(x6 - x2 = 6\) 说明$ x2 = 4\(。**但是\)x1\(和\)x2\(距离为4,\)x2\(与\)x5$距离为4,距离表中没有两个4,矛盾**
x4 = 7的道路不同,回溯到x5 = 8, 向下选取另一条道路x2 = 3
后续的最大值变为6,尽可能出现在\(x1\)到\(x4\)和\(x3\)到\(x6\),得到两个情况\(x4 = 6\)或者\(x3 = 4\)
对于\(x3 = 4\),\(x1\)到\(x3\)的距离,\(x3\)到\(x5\)的距离都是4,矛盾
只剩下\(x4 = 6\),后续只可能出现 x3 = 5
最终得到结果(0,3,5,6,8,10)
代码实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 200
int Get_num(int n)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(n == i* (i-1) / 2)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
bool Reconstruct1(vector<int> &path, vector<vector<int>> &solutions, multiset<int> &distances, int n, int left, int right)
{
// path是存放收费站位置的数组
// path[1], path[2],...path[left - 1]已知
// path[right + 1], ... path[n]已知
bool Found = false;
// 先判断distances是否为空,为空则找到最后的结果
if(distances.empty())
{
Found = true;
solutions.push_back(path);
return Found;
}
multiset<int>::iterator iter;
// 先找到目前distances中的最大值
int max_distance = *distances.rbegin();
// 选择一:path[right] = max_distance
// 此时max_distance 是 收费站 path[0]和path[right]的距离
path[right] = max_distance;
int distance;
// 计算当前right收费站与已知收费站之间的距离
// 将它们从multiset distances 中删除
int i;
for(i = 1; i < left; i++)
{
distance = path[right] - path[i];
iter = distances.find(distance);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
// 恢复原状,将已经删除的重新插入
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[right] - path[j]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == left)
{
for(i = right + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
distance = path[i] - path[right];
iter = distances.find(distance);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
// 恢复原状,将已经删除的重新插入
for(int j = 1; j < left; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[right] - path[j]);
}
for(int j = right + 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[j] - path[right]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == n + 1)
{
// 进入下一轮的递归
Found = Reconstruct1(path, solutions, distances, n, left, right - 1);
if(!Found)
{
for(int k = 1; k < left; k++)
distances.insert(path[right] - path[k]);
for(int k = right + 1; k <= n; k++)
distances.insert(path[k] - path[right]);
}
else
Found = true;
}
}
if(Found == false)
{
// 选择二:path[n] - path[left] = max_distance
// path[left] = path[n] - max_distance
path[left] = path[n] - max_distance;
// 如上删除新的distance
for(i = 1; i < left; i++)
{
iter = distances.find(path[left] - path[i]);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[left] - path[j]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == left)
{
for(i = right + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
iter = distances.find(path[i] - path[left]);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
for(int j = 1; j < left; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[left] - path[j]);
}
for(int j = right + 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[j] - path[left]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == n + 1)
{
Found = Reconstruct1(path, solutions, distances, n, left + 1, right);
if(!Found)
{
for(int k = 1; k < left; k++)
distances.insert(path[left] - path[k]);
for(int k = right + 1; k <= n; k++)
distances.insert(path[k] - path[left]);
}
else
Found = true;
}
}
}
return Found;
}
bool Reconstruct2(vector<int> &path, vector<vector<int>> &solutions, multiset<int> &distances, int n, int left, int right)
{
// path是存放收费站位置的数组
// path[1], path[2],...path[left - 1]已知
// path[right + 1], ... path[n]已知
bool Found = false;
// 先判断distances是否为空,为空则找到最后的结果
if(distances.empty())
{
Found = true;
solutions.push_back(path);
return Found;
}
multiset<int>::iterator iter;
// 先找到目前distances中的最大值
int max_distance = *distances.rbegin();
int i;
// 选择二:path[n] - path[left] = max_distance
// path[left] = path[n] - max_distance
path[left] = path[n] - max_distance;
// 如上删除新的distance
for(i = 1; i < left; i++)
{
iter = distances.find(path[left] - path[i]);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[left] - path[j]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == left)
{
for(i = right + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
iter = distances.find(path[i] - path[left]);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
for(int j = 1; j < left; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[left] - path[j]);
}
for(int j = right + 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[j] - path[left]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == n + 1)
{
Found = Reconstruct1(path, solutions, distances, n, left + 1, right);
if(!Found)
{
for(int k = 1; k < left; k++)
distances.insert(path[left] - path[k]);
for(int k = right + 1; k <= n; k++)
distances.insert(path[k] - path[left]);
}
else
Found = true;
}
}
if(Found == false)
{
// 选择一:path[right] = max_distance
// 此时max_distance 是 收费站 path[0]和path[right]的距离
path[right] = max_distance;
int distance;
// 计算当前right收费站与已知收费站之间的距离
// 将它们从multiset distances 中删除
int i;
for(i = 1; i < left; i++)
{
distance = path[right] - path[i];
iter = distances.find(distance);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
// 恢复原状,将已经删除的重新插入
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[right] - path[j]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == left)
{
for(i = right + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
distance = path[i] - path[right];
iter = distances.find(distance);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
// 恢复原状,将已经删除的重新插入
for(int j = 1; j < left; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[right] - path[j]);
}
for(int j = right + 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[j] - path[right]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == n + 1)
{
// 进入下一轮的递归
Found = Reconstruct1(path, solutions, distances, n, left, right - 1);
if(!Found)
{
for(int k = 1; k < left; k++)
distances.insert(path[right] - path[k]);
for(int k = right + 1; k <= n; k++)
distances.insert(path[k] - path[right]);
}
else
Found = true;
}
}
// 选择二:path[n] - path[left] = max_distance
// path[left] = path[n] - max_distance
path[left] = path[n] - max_distance;
// 如上删除新的distance
for(i = 1; i < left; i++)
{
iter = distances.find(path[left] - path[i]);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[left] - path[j]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == left)
{
for(i = right + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
iter = distances.find(path[i] - path[left]);
if(iter != distances.end())
{
distances.erase(iter);
}
else
{
for(int j = 1; j < left; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[left] - path[j]);
}
for(int j = right + 1; j < i; j++)
{
distances.insert(path[j] - path[left]);
}
Found = false;
break;
}
}
if(i == n + 1)
{
Found = Reconstruct1(path, solutions, distances, n, left + 1, right);
if(!Found)
{
for(int k = 1; k < left; k++)
distances.insert(path[left] - path[k]);
for(int k = right + 1; k <= n; k++)
distances.insert(path[k] - path[left]);
}
else
Found = true;
}
}
}
return Found;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
multiset<int> distances1;
multiset<int> distances2;
int x;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
distances1.insert(x);
distances2.insert(x);
}
// 利用distances的数量计算收费站的数量
int num = Get_num(n);
vector<int> path1(num + 1, -1);
vector<int> path2(num + 1, -1);
vector<vector<int>> solutions;
path1[1] = 0;
path1[num] = *distances1.rbegin();
path2[1] = 0;
path2[num] = *distances2.rbegin();
distances1.erase(path1[num]);
distances2.erase(path2[num]);
Reconstruct1(path1, solutions, distances1, num, 2, num - 1);
Reconstruct2(path2, solutions, distances2, num, 2, num - 1);
for(int i = 0; i < solutions.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= num; j++)
{
cout << solutions[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "Total number of solutions : " << solutions.size() << endl;
}
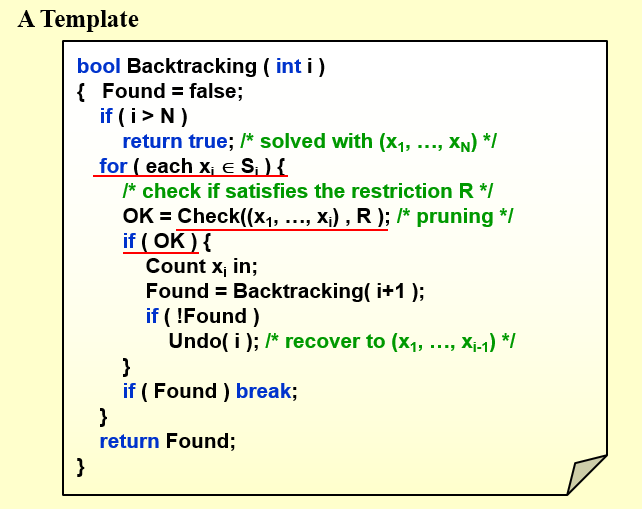
回溯算法的模板
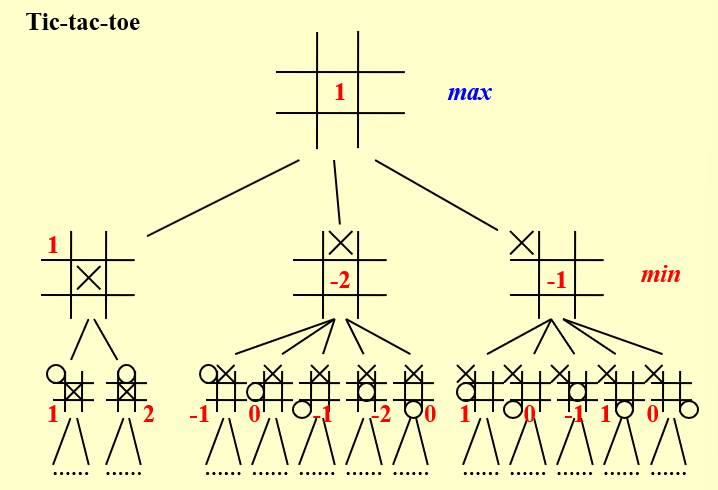
6.3 井字棋¶
-
AI下棋问题:需要推算出所有可能的情况并且选择当前胜率最高的情况往下走
-
MinMax Strategy问题(最大最小策略):
-
goodness函数\((f(P)=W_{AI}-W_{Human})\),W是当前情况下某一方可能赢的所有结果,不需要考虑另一方后面会怎么下,只要计算自己在当前局势下的任何可以赢的方法.
-
The human is trying to minimize the value of the position P, while the computer is trying to maximize it.
X表示机器下的位置, O表示人下的位置
最开始模拟最初的两步,AI先手,选择对自己最有利,也就是max的情况
机器会最大化\(f(P)\),所以第一轮机器会下在中心点
第二轮,人为了最小化\(f(P)\),将下在角落
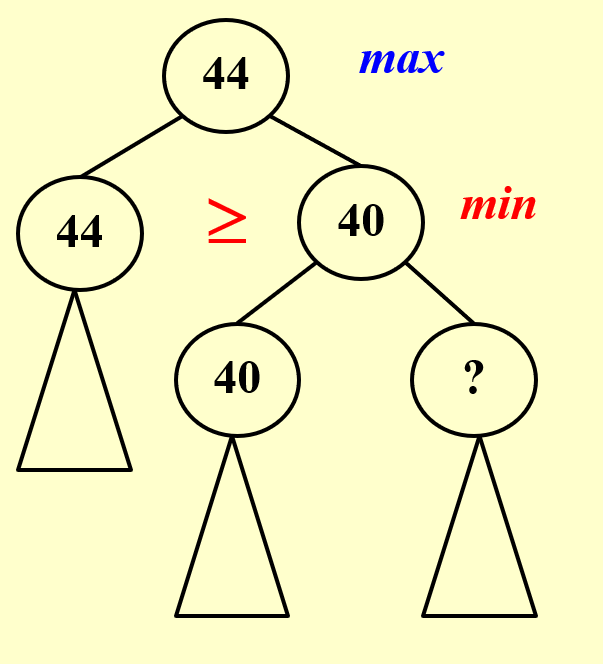
6.4 \(\alpha \beta\)剪枝搜索¶
AI在max处的选择,不需要考虑问号处的value。
因为 min层会选择小于等于的数作为结果,max必然会选择大于等于44的结果,也就没必要计算问号了
6.5 习题集¶
-
In the 4-queens problem,$ (x1, x2, x3, x4)$ correspond to the 4 queens’ column indices. During backtracking, (1, 3, 4, ?) will be checked before (1, 4, 2, ?), and none of them has any solution in their branches.
T首先检查1,3,4,发现不满足。然后检查1,4,开头的1,2,3,4,5,6…。首先从第一行往下检查,从左往右遍历。如果不满足,不进行下一行的检查。
-
In a Turnpike Reconstruction Problem, given distance set \(D = { 2, 2, 4, 4, 6, 8 }\),$ x1~x4 = ( 0, 2, 4, 8 )$ is the only solution provided that \(x1 = 0.\) 0,4,6,8也是可以的。按照那个算法:首先\(x4=8\)
然后找出D最大的为6,尝试\(x3=6\),发现8-6在D中。将2从D中删除
然后找D最大的为4,尝试\(x2=4\),发现8-4=4,6-4=2在D中,将2,4删除。
最后D为空,说明解决问题。
有一种解法,根据镜像就存在第二种解法
-
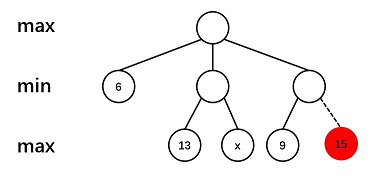
Given the following game tree, the red node will be pruned with α-β pruning algorithm if and only if __.
剪枝发生的情况:其兄弟节点比它的节点更优。它的另外一个子节点被剪枝。
此时,min选择了9,则为了比9更优,x必须大于9,才能使得中间一个节点无论如何大于9,则Max不会选择最右边节点。D
-
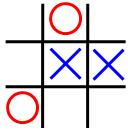
In the Tic-tac-toe game, a "goodness" function of a position is defined as \(f(P) = W_{computer} - W_{human}\)where \(W\) is the number of potential wins at position \(P\).In the following figure, O represents the computer and X the human. What is the goodness of the position of the figure?
-
A. -1
-
B. 0
-
C. 4
-
D. 5
X可以单走一步就是赢,X走两步赢的方法有两种
O走两步赢的方法有3种
3 - 3 = 0
-
-
Given the following game tree, which node is the first one to be pruned with α-β pruning algorithm?
-
A. a
-
B. b
-
C. c -
D. d
搜索到 b 等于 86 时,a处的值会大于86,而min层会选择小于等于68的结点,所以c点不需要再检测。
即 β 剪枝。
-