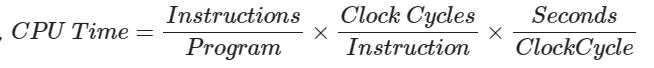1. Introduce¶
约 1419 个字 预计阅读时间 7 分钟
- 冯·偌伊曼架构
- 计算与存储分离
- 数据和指令放在同一个存储器
1.1 Eight Great Ideas¶
-
Design for
Moore’s Law(设计紧跟摩尔定律)- Moore's Law: Integrated circuit resources double every 18-24 months. 摩尔定律:集成电路资源每18-24个月翻一番。
- Design for where it will be when finishes rather than design for where it starts. 设计完成时的位置,而不是设计开始的位置。
-
Use
Abstractionto Simplify Design (采用抽象简化设计)- 层次化、模块化的设计
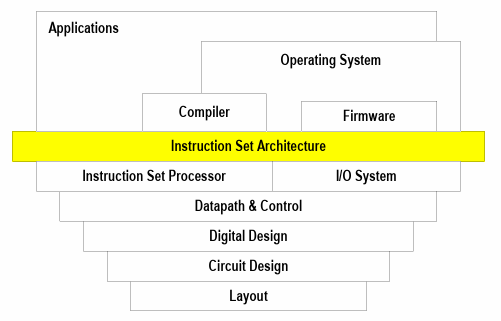
Instruction set architecture---- the interface between hardware and lowest-level software ISA 连接硬件与底层软件
-
Make the
Common Case Fast(加速大概率事件) -
Performance via
Parallelism(通过并行提高性能) -
Performance via
Pipelining(通过流水线提高性能)- 换句话说就是,每个流程同时进行,只不过每一个流程工作的对象是时间上相邻的若干产品;
- 相比于等一个产品完全生产完再开始下一个产品的生产,会快很多;
- 希望每一个流程的时间是相对均匀的;
-
Performance via
Prediction(通过预测提高性能)- 例如先当作
if()条件成立,执行完内部内容,如果后来发现确实成立,那么直接 apply,否则就再重新正常做; - 这么做就好在(又或者说只有这种情况适合预测),预测成功了就加速了,预测失败了纠正的成本也不高;
- 例如先当作
-
Hierarchy of Memories (存储器层次)
- Disk / Tape -> Main Memory(DRAM) -> L2-Cache(SRAM) -> L1-Cache(On-Chip) -> Registers
容量从左到右,依次减小;速度从左到右,依次增大
- Disk / Tape -> Main Memory(DRAM) -> L2-Cache(SRAM) -> L1-Cache(On-Chip) -> Registers
-
Dependability via Redundancy (通过冗余提高可靠性)
- 类似于卡车的多个轮胎,一个模块 down 了以后不会剧烈影响整个系统;
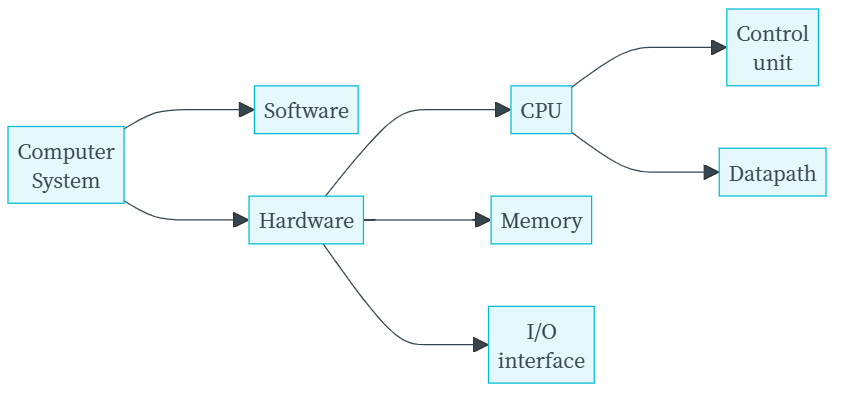
1.2 Below Your Program¶
- Application software : aimed at users
- System software : aimed at programming.
- 包含: Operation System;Compiler;Assembler
1.3 Computer Language¶
-
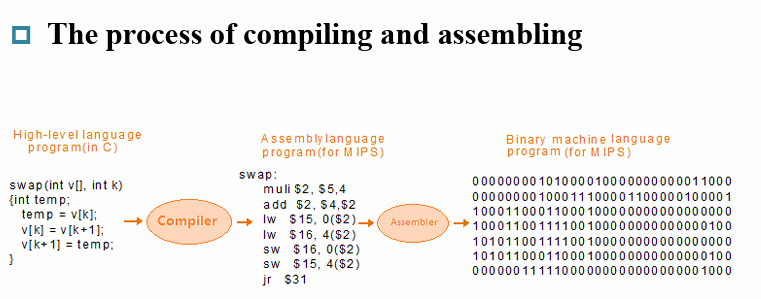
Machine language 机器语言
-
Binary numbers express machine instructions
ex. 1000110010100000 means to add two numbers
-
-
Assembly language 汇编语言
-
Symbolic notations
ex. add A, B
-
The assembler translates them into machine instruction
汇编器将汇编语言翻译为机器语言
-
-
High-level programming language 高级编程语言
-
Notations more closer to the natural language ex. A + B
-
The compiler translates them into assembly language statements
编译器将高级编程语言翻译为汇编语言
-
1.4 Computer Organization and Hardware System¶
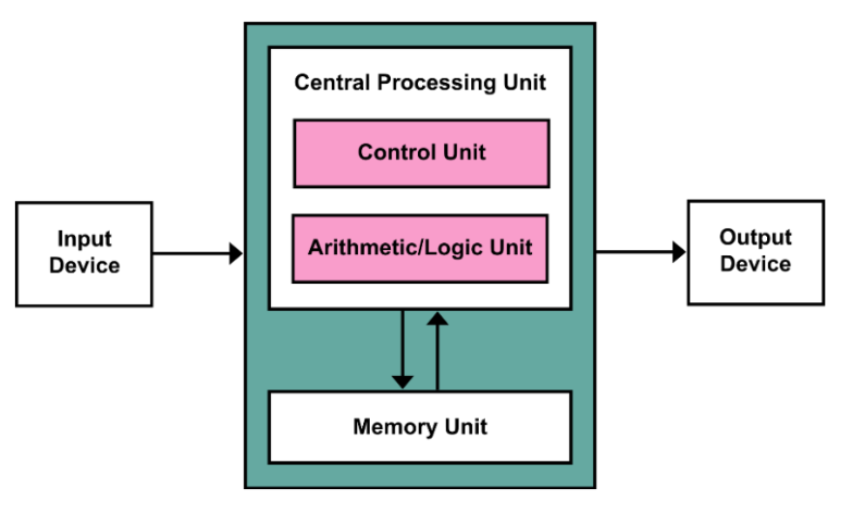
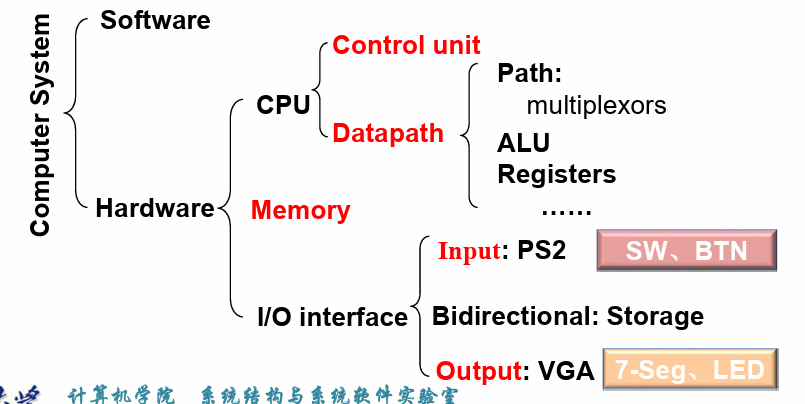
The five classic components of a computer: 计算机的五个经典组件:
- input;
- output;
- memory(DRAM);
- 程序、数据存储的地方,也是程序“运行的位置”;
- cache memory (SRAM): buffer for the DRAM memory;
- datapath
- 负责实际的数据处理;
- control
- 负责指挥控制如何进行数据处理,给出控制信号;
processor / (central processor unit)CPU = datapath + control处理器/(中央处理器单元)CPU = 数据路径 + 控制
1.6 Performance¶
1.6.1 Execution Time¶
-
Response time && Throughout
-
Response time / execution time: how long it takes to do a task响应时间: 从程序开始到结束的时间(个人)
-
Throughout: total work done per unit time
吞吐量:单位时间内完成的任务数量(服务器)
-
Replacing the processor with a faster version?
改变response time 和 throughoutAdding more processors ?
只改变throughout
-
定义\(performance = \dfrac{1}{Execution \ time}\)
X is n times faster than Y
$$ \dfrac{{Performance}_x}{{performance}_y} = \dfrac{{execution time}_y}{{execution time}_x} = n\ $$
\(也就是说x的运行时间是y的\dfrac{1}{n}\)
-
关于 Execution Time
-
Elapsed time
包含 Processing,I/O, OS overhead, idle time
-
CPU time
-
1.6.2 CPU Clocking¶
-
Clock period: duration of a clock cycle
\(eg:250ps = 0.25ns = 250 \times 10^{-12}s\)
-
Clock frequency (rate): cycles per second
\(eg:4.0GHz = 4000MHz = 4.0 \times 10^9Hz\)
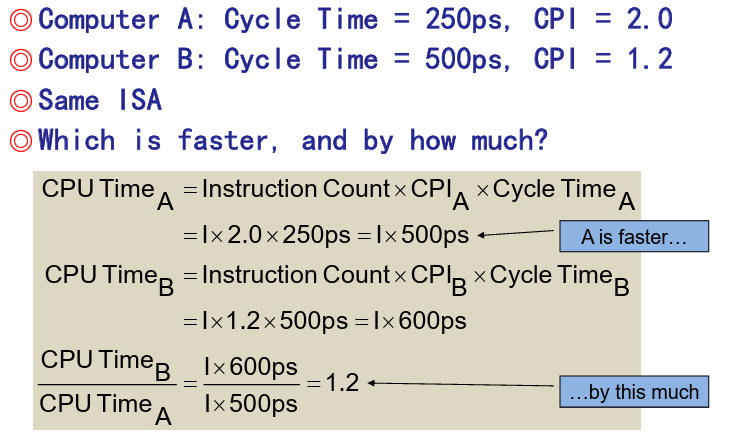
\[ \begin{aligned} CPU \ Time &= CPU \ Clock \ Cycles \times Clock \ Cycle \ Time \\ &= \dfrac{CPU \ Clock \ Cycles}{Clock \ Rate} \end{aligned} \]
Practice:
Computer A: 2 GHz clock, 10s CPU time
Designing Computer B :
Aim for 6 s CPU time ;
Can do faster clock, but causes 1.2 × clock cycle
How fast must Computer B clock be?
-
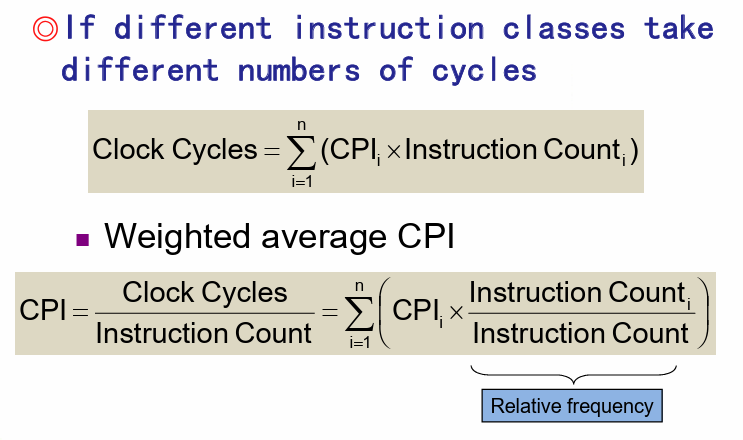
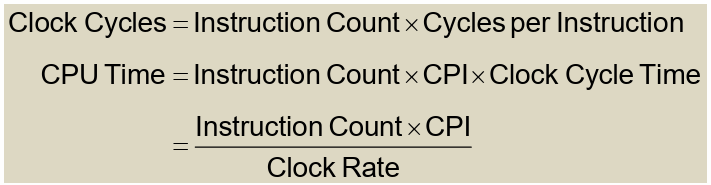
每条指令的平均周期数(Average cycles per instruction)又缩写为 CPI。
由CPU的硬件决定,不同的指令有不同的CPI $$ CPU Time = Instruction count \times CPI \times Clock cycle time $$
Performance depends on
- Algorithm: affects
IC(指令条数), possibly CPI - Programming language: affects IC, CPI
- Compiler: affects IC, CPI
- Instruction set architecture : IC,CPI,T_c(\(\dfrac{Seconds}{ClockCycle}\))
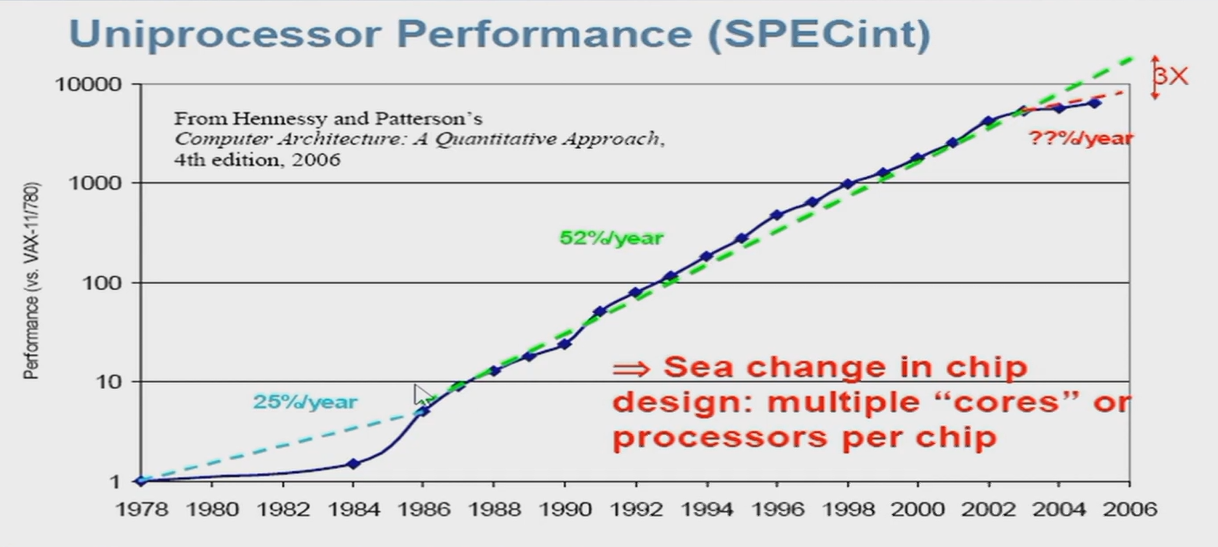
1.7 Incredible performance improvement¶
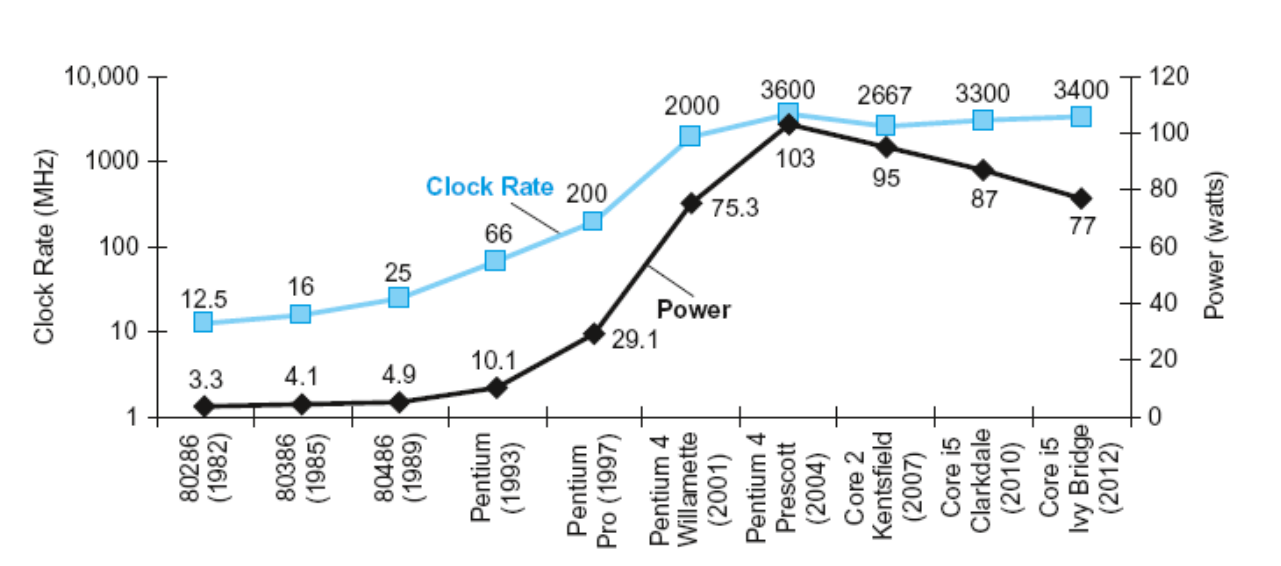
-
Power Wall
\(Power = Capactive \ load \times {Voltage}^2 \times Frequency\)
频率 负载电容 电压 频率
主频提高了很多,但功耗并没有得到这么多的提升,因为我们降低了工作电压 (5V-1V)
电压不能一味下降,会造成电流过大,引发功耗浪费
-
Memory Wall
Memory 的性能增长不如 CPU 的性能增长,大部分时间花在读写内存了,影响整体性能
-
ITP Wall(指令集并行)
refers to increasing difficulty to find enough parallelism in the instructions stream of a single process to keep higher performance processor cores busy.
很难在单个进程的指令流中找到足够的并行度,以保持更高性能的处理器内核繁忙。
\(ITP \rightarrow TLP \ and DLP\)
从指令集成到线程集成+数据集成
1.8 Multiprocessors 多核¶
-
Amdahl's Law: Improve an aspect of a computer and expecting improvement in overall performance.
阿姆达尔定律:改进计算机的某个方面,并期望整体性能得到改善。 实际上, \(T_{improve} = \dfrac{T_{affected}}{improvement \ factor} + T_{unaffected}\)
e.g.** 对某一方面优化 90%, 并不能使 CPU 整体性能优化 90%. Corollary: make the common case fast. 推论:使常见情况快速。**
-
Low Power Not at Idle.
低功耗,不处于空闲状态。 机器在没有工作时也有功耗损失。
-
MIPS as a Performance Metric
MIPS 作为性能指标,不同的 ISA 之间不能仅凭 MIPS 比较。
-
MIPS: Millions of Instructions Per SecondMIPS:每秒数百万条指令
\[ \begin{aligned} MIPS &= \dfrac{Instruction \ count}{Execution time \times 10^6} \\ &=\dfrac{Instruction \ count}{CPI \times Instruction \ count \times cycle \ clock\ time \times 10^6}\\ &= \dfrac{clock \ rate}{CPI \times 10^6} \end{aligned} \]
唯一的性能标准是CPU Time,不同的 ISA 之间不能仅凭 MIPS 比较。
-